Fire resistant low cost inorganic ceramic composites
←
→
Trascrizione del contenuto della pagina
Se il tuo browser non visualizza correttamente la pagina, ti preghiamo di leggere il contenuto della pagina quaggiù
w COMPOSITES - BUILDING
Fire resistant low cost inorganic ceramic composites
L.Giorgini (Università di Bologna - CIRI-MAM), L. Laghi (CertiMac, Faenza), V. Medri (ISTEC-CNR, Faenza),
C. Mingazzini* (ENEA TEMAF, Faenza), P. Bernardelli – CENTURIA, Faenza
Increasing fire-resistant materials and cost-effectiveness in the choice of an environmental and economic sustainability.
performances is possible only developing insulating system, doubts may be raised about One need only think that in the building sector,
new fiber reinforced inorganic composites. the perspectives of durability of these materials the “Minimum Environmental Criteria” (C.A.M.)
Recent news reports have highlighted how, in and their recyclability, the latter representing an have entered into force. These criteria set limits
the building sector, some of the vulnerabilities issue on which the attention of current legislation and restrictions on public contracts regarding
in terms of fire safety related to the energy is increasingly focusing, in a perspective of the environmental sustainability of the employed
efficiency improvements in buildings have materials and of the processes
been somehow underestimated. adopted in the building site.
The use of porous materials and crawl Some examples regarding this
spaces, although undoubtedly advantageous are mentioned, such as:
in terms of thermal insulation, may be the - arrangement of a selective
origin of critical situations whenever, after the demolition practice in order to
installation, these porosities host materials and/ foster the efficient recycling of
or unexpected living organisms (notably the waste materials,
case of wasps) which, also after rehabilitation, - A minimum limit of 15% of the
bring fuel material in inaccessible dry and well total amount of the employed
aerated places, worsening the fire resistance materials as far as the recycled
progressively over time. materials are concerned.
If the polymer foam solution represents - A push to obtain the documents
the best compromise in terms of lightness of the materials used. These
Materiali compositi inorganici di basso costo, resistenti a fuoco
L.Giorgini (Università di Bologna - CIRI-MAM), L. Laghi (CertiMac, Faenza), V. Medri (ISTEC-CNR, Faenza),
C. Mingazzini* (ENEA TEMAF, Faenza), P. Bernardelli – CENTURIA, Faenza
L’incremento della resistenza aL fuoco finiscano con l’ospitare materiali e/o organi- legate al riciclo, un aspetto che sempre di più
dei materiali da costruzione è possibi- smi viventi imprevisti (degno di nota è il caso si sta collocando al centro dell’attenzione nella
le solo sviluppando nuovi materiali compositi ad esempio dei nidi di vespe). Tali materiali, normativa vigente, in una prospettiva di so-
inorganici. anche successivamente a bonifica, possono stenibilità ambientale ed economica circolare.
Recenti fatti di cronaca hanno messo in introdurre sostanze conbustibili in posizioni Basti pensare, uno su tutti, che in ambito
evidenza come in edilizia si sia in qualche spesso inaccessibili, asciutte e ben areate, edilizio sono entrati in vigore i “Criteri Am-
modo sottovaluta la vulnerabilità in termini peggiorando progressivamente nel tempo la bientali Minimi” (C.A.M.) che pongono vincoli e
di sicurezza al fuoco legata agli interventi di resistenza all’incendio. prescrizioni, per la partecipazione agli appalti
efficientamento energetico dell’edificio. Se la soluzione delle schiume polimeriche pubblici, per quanto concerne la sostenibilità
L’uso di materiali porosi ed intercapedini, rappresenta, ad oggi, il miglior compromesso ambientale dei materiali utilizzati e dei pro-
se indubbiamente vantaggioso in termini di in termini di leggerezza ed economicità nella cessi messi in atto in cantiere. Si citano solo
isolamento termico, può essere all’origine di scelta di un sistema isolante, non pochi dubbi alcuni esempi al riguardo:
potenziali criticità laddove, in tempi succes- si potrebbero sollevare circa le prospettive di - predisposizione di un iter di demolizione se-
sivi all’installazione, dette porosità o cavità durabilità di questi materiali e le problematiche lettiva al fine di favorire il riutilizzo efficiente
12 composite solutions & technopolymers n. 1/2018w COMPOSITES - BUILDING
documents have to be employed for these applications and
adequate to certify the temperatures. Project EEE-CFCC
content of the recycled material, partners are all located in Faenza
through environmental declarations technopole and include ISTEC-CNR,
of Class I, II or III (EPD). In this way, the CIRI-MAM, CertiMaC and Centuria
LCA analysis of all the components under the coordination of ENEA
employed in the work is facilitated. TEMAF. The experimental program
- The EEE-CFCC project (www.eee- aims at developing the associtation
cfcc.it, POR FESR Emilia Romagna of BasKer with an inorganic and fire
2014-2020) focuses its research resistant porous core, for applications
and development activities on fiber- to fire doors and fire resistant thermally
reinforced inorganic composite insulating panels. This porous core,
materials for building and transportation of a pre-ceramic polymer. The material was up to ISTEC CNR, is developed from secundary
applications. The starting point was the called BasKer (Basalt-Ceramic) to summarize raw materials by means of a geopolimerisation
development, at the ENEA-TEMAF laboratories its chemical nature. reaction (that is an alkaline activated consolidation,
in the frame of the MITAI Technopole of Faenza The developed prepreg-derived basalt reinforced according to the presented scheme).
(POR-FESR Emilia Romagna 2011-2013), composite appears of potential high interest for
of a completely inorganic fiber reinforced fire resistant applications. Main characteristics are THERMAL MODELING AND FIRE TESTING OF
composite produced from basalt fibers bonded a density below 2g/cm3, creep resistance (to its THE COMPOSITE SOLUTION
with a ceramic matrix, obtained by pyrolysis own weight) up to 1200°C and a good insulation Regarding its ability to thermally shield the
(thermal treatment in an inert atmosphere) capacity, better than with the materials typically action of a fire load, the combined system
dei materiali di risulta, cofinanziato dalla Regione Emilia Romagna, una matrice ceramica, ottenuta per pirolisi
- Limite minimo del 15% sul totale dei Bando POR-FESR 2014-2020) pone al centro (trattamento termico in ambiente inerte) di
materiali utilizzati per quanto riguarda i ma- della sua attività di ricerca e sviluppo proprio un polimero preceramico. Il materiale è stato
teriali riciclati, i materiali inorganici compositi fibrorinforza- denominato BasKer (Basalto- Ceramica) per
- Spinta all’ottenimento, per i materiali impie- ti, per applicazioni nel campo dell’edilizia e riassumerne la natura chimica.
gati, di documentazioni idonee a certificare il dei trasporti. Il punto di partenza è stato lo Questo composito è parso subito come un
contenuto di riciclato attraverso Dichiarazioni sviluppo, presso i laboratori di ENEA-TEMAF, materiale di elevato interesse per applicazioni
Ambientali di categoria I, II o III (EPD) così nell’ambito del Tecnopolo MITAI di Faenza antifuoco. Le principali caratteristiche sono una
da favorire l’analisi LCA di tutti i componenti (POR-FESR Emilia Romagna 2011-2013), di densità inferiore a 2g/cm3, la capacità di reg-
impiegati nell’opera. un composito fibrorinforzato totalmente inor- gere almeno il proprio peso fino a 1200°C, una
- Il progetto EEE-CFCC (www.eee-cfcc.it, ganico, prodotto da fibre di basalto legate con buona capacità di coibentazione se paragonato
con altri materiali tipicamente
utilizzati per l’esposizione a
tali intervalli di temperatura. I
partner scientifici del progetto
EEE-CFCC (tutti appartenenti al
polo tecnologico di Faenza) sono
ISTEC-CNR, CIRI-MAM, CertiMaC
e Centuria, con il coordinamento
di ENEA-TEMAF.
Il programma punta ad asso-
ciare il BasKer a un core poroso
inorganico ed ignifugo, per
composite solutions & technopolymers n. 1/2018 13w COMPOSITES - BUILDING
(sandwich composite) “requirements of reaction to
can be modeled, in a fire“. This standard sets the
predictive way by means of test methods to check the fire
unsteady FEM models and on reaction class of interest (e.g.
the basis of the experimental Class A1 – totally fire-resistant
characterization up to high material, Class F – easily
temperature (above 1000 flammable material).
°C) of the thermo-physical Class A1 testing involves
parameters of each material exposure for 30 minutes at
constituting it (BasKer and 750°C in air, with recording
porous “geopolimers”). of any flame trigger (which,
In particular, the thermal for these materials, does not
conductivity (see the picture), occur), oxygen consumption
the thermal diffusivity and and heat development. The
the specific heat (these tests were performed by
parameters are essential to means of a conecalorimeter
describe the thermal behaviour from the CIRI MAM partner and
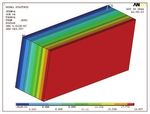
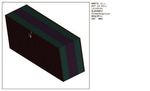
of the system under steady state conditions and In the first picture the discretization of the real they showed that (1) this solution falls into class
in the transient, that is during the development multilayer by means of finite volume elements A and (2) the two materials, jointed together with
of the fire) are determined through specific is depicted, whereas in the second picture the a geopolymeric adhesive, retain their shape and
measurement techniques (Heat flow meter, DSC temperature distribution (shape of the isotherms) consistency at the end of test, demonstrating a
analysis, Laser Flash analysis). This activity is along the panel thickness before the fire and proven stability with respect to the external fire.
carried out by the CertiMaC partner. under steady state heat transfer conditions is ENEA is designing the pilot lines for Basker
For example, some pictures are shown, which reported. panels up to 2 m2, a pyrolysis oven with a usable
are preliminary of the ongoing modeling activity The EN 13501-1 is the reference standard size of 1 m2 and a production line for a ceramic
and in which the section of a multilayer panel for the future application of the sandwich prepreg starting directly from the basalt fabric
undergoing a fire load is represented. composite in the building sector regarding the coil and ENEA’s original preceramic formulation.
applicazioni coibenti/antifuoco come e “geopolimeri” porosi); in particolare deter- con l’ausilio di tecniche di misura specifiche
porte e pannellature. Il materiale minandone conducibilità termica, diffusività (termoflussimetria, DSC, analisi Laser Flash),
poroso, di competenza di ISTEC-CNR, è pro- e calore specifico (parametri essenziali per attività svolta dal partner CertiMaC.
dotto da materie prime seconde adatte per qualificare il comportamento termico del siste- Si riportano a titolo di esempio alcune imma-
la geopolimerizzazione (cioè una reazione di ma in condizioni stazionarie ed al variare del gini preliminari delle attività di modellazione
consolidamento chimico alcalino, come nello tempo, ossia durante l’evolversi dell’incendio) in corso, in cui si evidenzia una sezione del
schema precedentemente riportato).
MODELLAZIONE TERMICA E TEST
DIREZIONE AL FUOCO
Il sistema combinato (composito sandwich)
può essere modellato in via predittiva per
quanto concerne la sua capacità di scher-
mare termicamente l’azione di un carico di
incendio mediante modelli di calcolo FEM
non stazionari e sulla base della caratterizza-
zione sperimentale fino ad alta temperatura
(oltre 1000 °C) dei parametri termo-fisici dei
singoli materiali che lo costituiscono (BasKer
composite solutions & technopolymers n. 1/2018w COMPOSITES - BUILDING
Regarding the costs, BasKer industry, fire-resistant thermal insulation is of
seems to fully meet the target of great importance also for the collective transport
traditional polymeric composite materials, sector (ships and trains) and automotive, where
and the combination with the anti-buckling lightening currently targets materials such as
geopolymer core allows to minimize polymer composites and light alloys, which
the thickness, while guaranteeing good should be isolated from potential sources of heat
mechanical properties. Geopolymers are and fire trigger. In addition, the ever-increasing
recognized as competitive construction use of batteries, with their statistical defects,
materials compared to traditional cementitious entails a real risk of accidental fire.
ones in terms of costs (if produced from
second raw materials) but superior as for Other contributing autors / Hanno contribuito
thermal performances and durability. Both the come autori”:
Basker and the geopolymer can be recycled at - P. Fabbri, F. Bezzi, F. Mazzanti, M.Scafè –
end-of-life, returning them to non-toxic inerts, ENEA -TEMAF, Faenza.
still appealing in the construction - E. Landi, A. Natali Murri,– ISTEC-CNR,
industry. Other and more specific Faenza.
processes of recycling and reuse - S. Bandini, G. De Aloysio – CertiMac, Faenza.
are currently being studied. - E. D’Angelo, G. Zattini – Dipartimento di
Chimica Industriale “Toso Montanari”,
OTHER POSSIBLE APPLICATION Università di Bologna – Centro Interdipar-
FIELDS timentale di Ricerca Industriale Meccanica
In addition to the construction Avanzata e Materiali (CIRI-MAM).
pannello multistrato sottoposta a cari- cono calorimetro dal partner CIRI MAM e materiali da costruzione competitivi rispetto
co di incendio. hanno dimostrato che (1) questa soluzione ai materiali cementizi tradizionali in termini di
Nella prima immagine è riportata la discre- ricade in classe A e che (2) i due materiali, costi (se prodotti da materie prime seconde),
tizzazione del multistrato reale in elementi di incollati fra loro con un adesivo anch’esso ma superiori come performance termiche e
volume finito, mentre nella seconda è riportata geopolimerico, mantengono forma e consi- durabilità. Entrambi i materiali possono es-
la distribuzione delle temperature (andamento stenza al termine del test, a dimostrazione di sere riciclati a fine vita, riportandoli ad inerti
delle isoterme) lungo lo spessore del pannello una comprovata stabilità rispetto all’azione atossici, nuovamente di interesse nel settore
prima dell’incendio, in condizioni di scambio esterna del fuoco. costruzioni. Altri e più specifici processi di
termico stazionario. ENEA sta predisponendo le linee pilota per la riciclo e riuso sono al momento allo studio.
La normativa di riferimento per la futura ap- realizzazione di pannelli in BasKer fino a 2 m2,
plicazione del composito sandwich in ambito un forno di pirolisi con dimensioni utili di 1 m2 ALTRI POSSIBILI AMBITI DI APPLICAZIONE
edilizio in materia di “requisiti di reazione al e una linea per la produzione del Prepreg Pre- Oltre che nell’industria delle costruzioni, le te-
fuoco”, è la EN 13501-1, che fissa i metodi di ceramico a partire direttamente dal rotolo di matiche della coibentazione termica resistente
prova per la verifica della classe di reazione al tessuto di basalto e dalla propria formulazione al fuoco sono di grande rilevanza anche per
fuoco di pertinenza dei materiali (ed: Classe preceramica originale. il settore dei trasporti collettivi (navi e treni)
A1 – materiale totalmente ignifugo, Classe F – Relativamente ai costi, il BasKers sembra e dell’automotive, dove attualmente l’allegge-
materiale facilmente infiammabile). soddisfare pienamente il target dei mate- rimento punta su materiali, come i compositi
La verifica della Classe A1 prevede l’espo- riali compositi polimerici tradizionali, e la polimerici e le leghe leggere, che andrebbero
sizione per 30 minuti a 750°C in aria, con combinazione con il core geopolimerico isolati dalle potenziali fonti calore e di innesco
registrazione dell’eventuale innesco di fiam- antibuckling permette di ridurre al minimo al fuoco.
ma (che, per i materiali in questione, non gli spessori, pur garantendo buone proprietà Inoltre l’uso sempre più massiccio di batterie,
avviene), il consumo di ossigeno e lo sviluppo meccaniche. con la loro difettosità statistica, comporta un
di calore. I test sono stati effettuati mediante I geopolimeri sono riconosciuti come rischio reale di incendio accidentale.
composite solutions & technopolymers n. 1/2018 15Puoi anche leggere